While the Netherlands is renowned for its windmills, tulips, canals, and bike riding, it's not often associated with camera manufacturing. However, it's home to some unique camera companies, including the popular Cambo. In fact, there were around 20 camera manufacturers in the country, such as Philips, which I've previously featured in a blog post, and other lesser-known companies like Tahbes, Foka, and a few smaller ones.
My connection to these cameras is quite recent, as I was drawn to them by their vibrant colors. As I've shared in previous posts, I have a fondness for colored cameras, a fascination that still holds true today. Whether it's a blue, green, rose, or any other uniquely colored camera, I'm immediately captivated and feel a strong desire to own it. In this case, I was fortunate to acquire two cameras-a striking green one with a black faceplate, and a brown version with a matching faceplate.
After doing a little digging on the camera and company, I found that the two I purchased were also different models. The brown camera is the Vena Venaret due to the accessory shoe on the top of the camera, while the green is the Vena Venaret Jr., the same model but without the accessory shoe. The good news is that the Venaret Jr. I purchased has a leather fitted case that was in excellent condition, and it is the model I shot in the blog post.
The Company:
Vena Optical Devices was founded in Amsterdam in 1940 by Evert Verlegh and Samuel Naarden. The company's name is a mixture of the starting letter from each founder's last name: VE from Verlegh and NA from Naarden. It was a difficult time to start a company due to the war, as Samuel was making optical lenses for Old Delft Company. While many of the company's Jewish employees were deported, it was difficult for them to do anything regarding the cameras made until after WWII ended.
In 1948, Vena came out with the Venaret camera. According to the instruction manual, the camera was designed by F. Kochman, the former manufacturer of the Reflex-Korelle camera. Mr. Kochman was living in The Netherlands for a few years, was an employee of Vena, and designed the Venaret camera; according to the manual, "His long experience in the field of camera construction is already a guarantee for the good health of the newborn." With this knowledge, the Venaret looks similar to the Reflex-Korelle camera, although a much simpler version.
The Venaret had a few different versions. The camera was produced with a black faceplate and black covering, a white faceplate with black covering, or a brown faceplate and brown covering, which is the model I recently received.
The Venaret Jr. camera has a white faceplate with a black covering, a black faceplate with a black covering, and a white faceplate with a green covering, and the model I recently received has a black faceplate with a green covering.
In 1949, Vena produced a couple of straightforward box cameras, the Vena Box and Sport Box. It's estimated that Vena produced between 20,000 and 30,000 cameras before it went bankrupt and closed its doors in 1951. This was a very short-lived camera company, but it produced some brightly colored and very simply designed cameras.
My Camera:
My camera is 5.25" wide by 3.5" tall, including the viewfinder, 3 3/8" deep, and weighs 14.9 oz. and has a very cube shape. There are two shutter speeds on the camera, 1/25 and 1/50, along with "T" for timed exposures. The camera has a 75mm f7.7 Meniscus lens with four aperture settings, F7.7, F9, F11, and F16. The shutter speeds are set with a toggle switch above the lens with the "T" setting in the middle. The aperture settings are on the side of the lens. The shutter release is on the right side of the camera. There is no cocking of the shutter. Pressing down the shutter lever to take the photo is very simple.








To open the camera to load the film is easy once you figure it out. On top of the camera is a sliding lever. Slide it to the "O" or open position. Grab the lens protruding area and pull up from the back of the camera. There is a small channel that the front of the camera slides into that allows the front of the camera to slide out of, which exposes the film camera where you can load or unload the film, depending on if all photos are taken. Once the film is loaded or unloaded, put the ridge of the back of the camera into the channel on the front and slide down until the top fits snuggly into the back, then slide the lever on the top to the right to lock the camera while taking photos.
There is no lens focusing, and the minimum focus is approx. 3 meters, about 10'. I found this out when I processed the negatives after taking the camera out and shot with it on a sometimes sunny afternoon, which was rare in the Portland area in November. Looking at the photos, I initially thought 3' was the minimum focus, but those images are blurry while the background is sharp. After I thought about it, I realized that many cameras that don't have focus ability have a "close up" filter or lens when you want to take photos from 1-3 meters, so that mistake was on me.
Note the shutter speed and aperture settings.
This is a very simple camera without many bells or whistles, but I wanted to shoot with it to see how it performed. In today's cameras, this would be considered a "point and shoot" style, with minimal settings and no focus ability.
My Results:
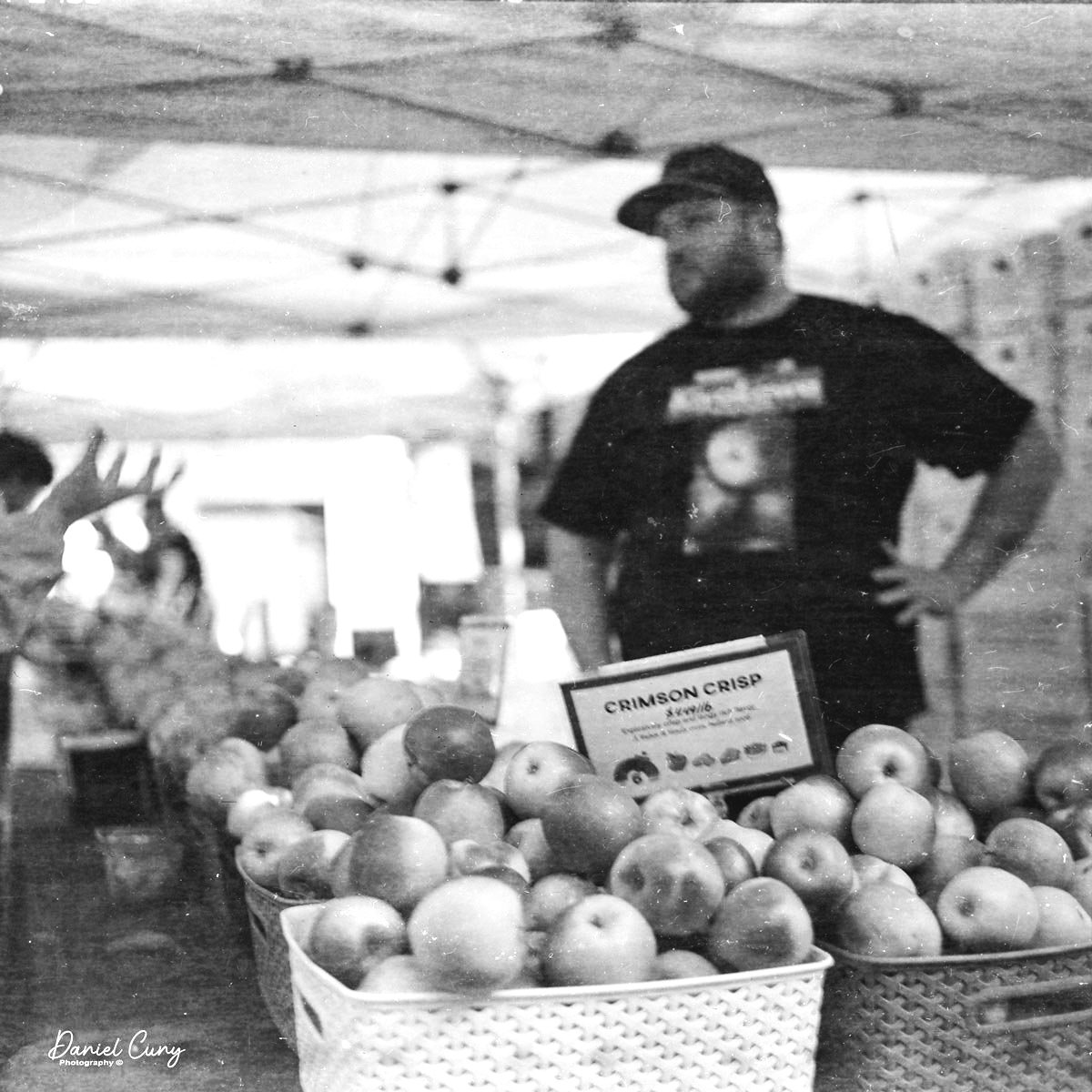
After putting in a roll of film, walking through the neighborhood, and taking simple, composed images, I went to my darkroom to process the negatives and see the results.
Here are a few of the images I took with this colorful gem of a camera:
Conclusion:
Except for my thinking the camera would focus closer than 10', the images are relatively sharp and clean. I didn't purchase these cameras, but I wanted to see how sharp they could produce, and they were pretty decent.
Thank you for taking the time to delve into the history of this short-lived camera company from a country not typically associated with camera manufacturing. Despite its brief existence, Vena Optical Devices managed to create a truly beautiful and functional camera.
Until next week, please be safe.