My Minolta-35, Model II
The Minolta-35 Model II camera I have was an unexpected discovery, purchased with several other cameras through an online auction. It wasn't the camera I was originally after in the lot, but the only thing that distinguished it in the photo was the fitted case, with 'Minolta' proudly displayed on the face.
There were so many different models of camera from Minolta during this timeframe that I wasn't sure what was actually in the fitted case. Still, when I received the "lot" of cameras and uncased the Minolta-35, someone had painted the camera black. And whoever painted it did an abysmal job of it. I only wish I had photos of the camera in that state, but I didn't think of it then. The camera was painted black, and the shutter wasn't working. The good news is that the camera had a good and clean lens.
Over the years, I have brought the camera to a few different collectible camera shows in hopes of selling it, but no sales have been made.
One day, a few months ago, I was browsing the cameras on my shelf, looking for one to write about, when I picked up the Minolta. I felt a personal connection to it, and determined to do a blog post, I sent it off to my trusty camera technician, Allen, at CameraWerks in NY to have it CLA'd. Despite its modest value, the fact that it's from the early 1950s and a very respectable Leica thread mount 'clone' made it worth the investment for me.
My Minolta-35, Model II with case.
Before I sent the camera to Allen, I wanted to get the black paint off the camera and bring it back to the original chrome camera it was. I had bought some Acetone to see if I could gently get rid of the paint and not ruin any of the other parts of the camera. Unfortunately, the Acetone didn't work well and didn't take much of the paint off. Then, I noticed that if I used my fingernail, the paint would chip off reasonably easily. I also noticed that in our kitchen, we had some bamboo skewers, which seemed to work OK, so to get into some of the tighter spots, I used the bamboo skewer, and to get into the very tight areas, I used the tip of some of the metal tweezers I have for some very minor repairs.
The camera still has some very minor spotting of black paint, as you'll see in the photos in the article, but 99.8% of the paint is gone. The camera looks considerably better than it did before. It's in great working condition, and even the rangefinder is clean and accurate, so it was time to do my blog on this early Minolta 35mm rangefinder camera.
The Company:
Minolta was a pioneering Japanese camera manufacturer known for its innovative contributions to photography. Founded in 1928 as Nichi-Doku Shashinki Shōten (which translates to "Japanese-German Camera Company"), the company was renamed Minolta in 1933. The name Minolta is derived from "Mechanismus, Instrumente, Optik und Linsen von Tashima," reflecting its German-Japanese technological collaboration.
Ad for Minolta 35 camera.
Minolta's early cameras were heavily influenced by German designs, particularly Leica and Contax rangefinders. The company released its first camera, the Nifcarette, in 1929, followed by various medium-format folding cameras in the 1930s. After World War II, Minolta resumed camera production, releasing the Minolta-35 in 1947, which became Japan's first 35mm camera with a coupled rangefinder.
Minolta's breakthrough came in 1958 with the Minolta SR-2, its first single-lens reflex (SLR) camera. Throughout the 1960s, the company expanded its SLR lineup, introducing the Minolta SR-T 101 in 1966, which featured an innovative through-the-lens (TTL) metering system. The 1970s saw Minolta partner with Leica, resulting in co-developed cameras like the Leica R3 and Minolta XE-7.
One of Minolta's most revolutionary releases was the Minolta XD-7 (XD-11 in North America) in 1977, the world's first camera with aperture-priority and shutter-priority automatic exposure modes. This technological advancement set the stage for further automation in cameras.
In 1985, Minolta changed the photography world with the Minolta Maxxum 7000 ( Alpha 7000 in Japan and Dynax 7000in Europe). This was the first SLR camera with fully integrated autofocus, making it far easier for photographers to achieve sharp images quickly. The Maxxum series gained popularity, pushing competitors like Canon and Nikon to accelerate their autofocus developments.
During the 1990s, Minolta expanded into digital imaging and compact cameras while maintaining its SLR dominance with the Dynax (Maxxum) series. The Minolta RD-175, released in 1995, was one of the earliest digital SLRs, marking Minolta's transition into the digital era.
In 2003, Minolta merged with Konica, another Japanese camera giant, to form Konica Minolta. However, due to declining camera sales, Konica Minolta exited the camera business in 2006, selling its assets, including the popular A-mount system, to Sony. This acquisition helped Sony establish itself in the DSLR market, leading to the Alpha series that continues today.
Though Minolta as a brand no longer produces cameras, its legacy lives on through Sony's Alpha series, which traces its roots back to Minolta's innovative technologies.
My Camera:
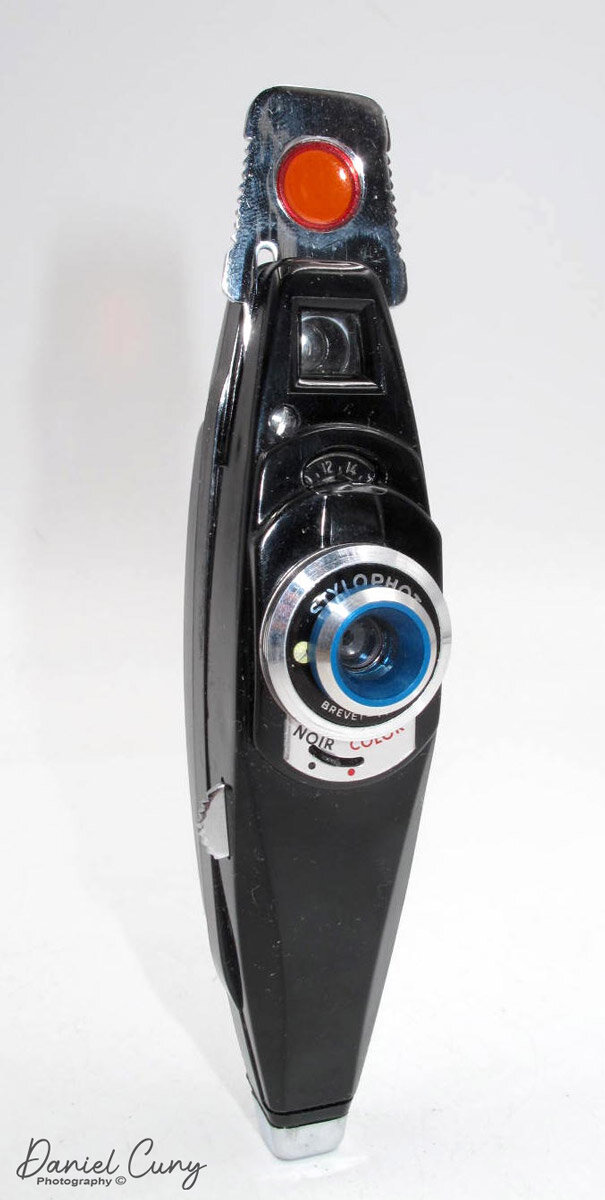
My Minolta-35, Model II is 5 3/8" wide by 3" tall by 3" deep, which includes the Chiyoko Super Rokkor 5cm (50mm) F2.8 lens. If I take the lens off, the body only is 1.5" deep. The camera weighs 1 lb. 10.9 oz is a very comfortable camera size and weight, and it fits into my hands nicely. The Minolta-35 Model II has shutter speeds ranging from 1/500 down to 1 second, with "T" for timed exposures and "B" for bulb.
The Minolta-35 Model II also splits the shutter speeds into two different dials on the camera with the higher speeds on the top dial, which go from 1/500 to 1/25 and "B" and from 1/25 to 1 sec, and "T" on the secondary shutter speed dial on the front of the camera just above the self-timer. To set the shutter speed, you'll need to lift up the dial and turn it to the desired speed for the exposure. Changing the shutter speeds should only be done once you cock the shutter.












To use the secondary or lower shutter speeds, the top dial needs to be set to 1/25, and the lower speed dial needs to be set at whatever of the slower speeds you'll be shooting. This method is prevalent for Leica copy cameras from this era.
The Chiyoko Super Rokkor lens on my Minolta-35 is smooth and in excellent condition. To focus, similar to other Leica thread mount lenses, a locking pin is used to lock the lens to the infinity position. To release the lock and focus to a closer range, press the release button and turn the lens to the desired focus distance. Inside the camera is a built-in rangefinder, which will aid the photographer in the distance needed to take a sharp photo. Along the outer rim of the lens is the lens's aperture ring, which goes from F2.8 to F22.
The shutter release is on the top of the camera, just to the right of the shutter speed dial. A small crown-shaped piece surrounds it, which can be removed to use a cable release for the timed or longer exposure times built into the camera.
Just above the shutter release is the rewind switch, which you slide to the "R" position to release the camera's drive gear so you can rewind the film back into the film canister when you complete the roll of film. Just to the right of the rewind switch is the film winding knob which has an arrow on top to show the user which direction to turn to advance the film to the next frame. At the bottom of the film winding knob is the frame counter which you need to zero out when you load a new roll of film into the camera so you'll know how many photos you've taken on the roll you loaded into the camera.
On the far left of the camera is the film rewind knob. Lift the knob up to make the rewinding of the film back into the film canisters easier. Once the back of the camera is open, you can lift the rewind knob even higher to remove or load the film canister in or out of the camera.
Right in the middle of the camera, on the top plate, is the Minolta-35 name along with the serial number, which on my camera is 90899, and Chiyoda Kogaku. I enjoy the modernistic font used on the older Minolta camera, which is very elegant.
Top plate with name on the Minolta-35, Model II camera.
On the back of the camera is the viewfinder window for focus, and on the outside is a dioptric adjustment. This is for people who wear glasses. Turning the dial around the finder window allows you to adjust your glasses prescription to correct vision issues. You can put the camera to your eye without wearing your glasses and still get a sharp photo. In the center of the back of the camera is the flash sync plug, which is just below the accessory shoe used for a flash attachment.
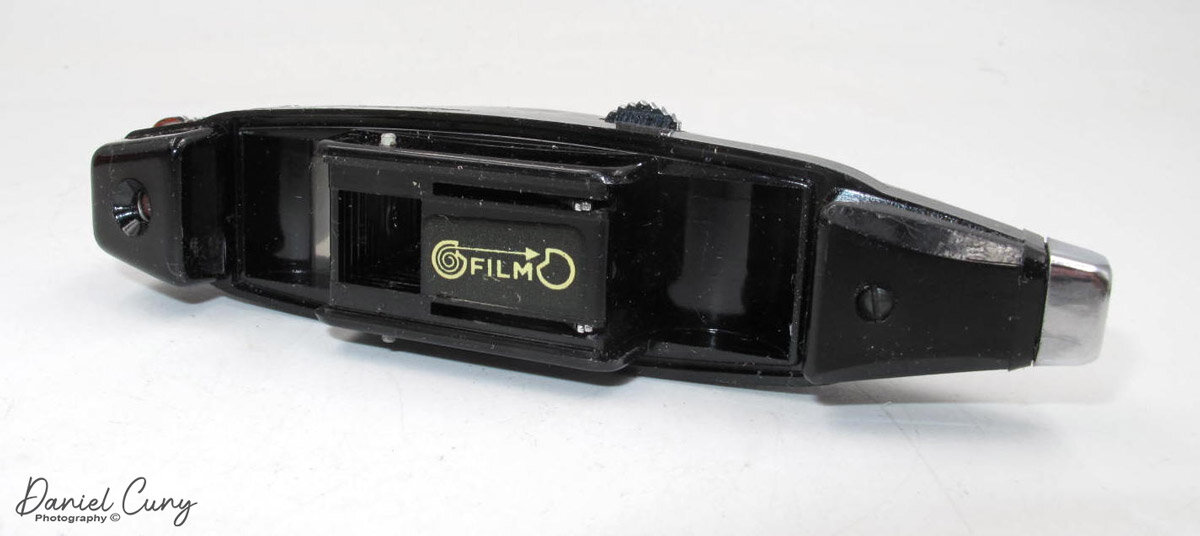
To open the camera to load film, there is a small knob on the bottom of the Minolta-35 that you'll need to turn counterclockwise until the "open" dot is lining up with the arrow. When this happens, the back of the camera springs open, and you load the camera just like you would any standard 35mm camera.
Lift the rewind knob to load the film cassette into the camera. Pull the leader across the drive gears and put the film leader into the slot on the take-up spool. Take the tension of the film up by turning the rewind knob clockwise to take the slack up on the film. Close the back turn the open/close knob to the "closed" position to lock the camera's back, and wind to your first frame. Watch that the rewind knob is turning when you advance the film so you know the film is transporting in the camera, and set the frame counter to number one.
My Results:
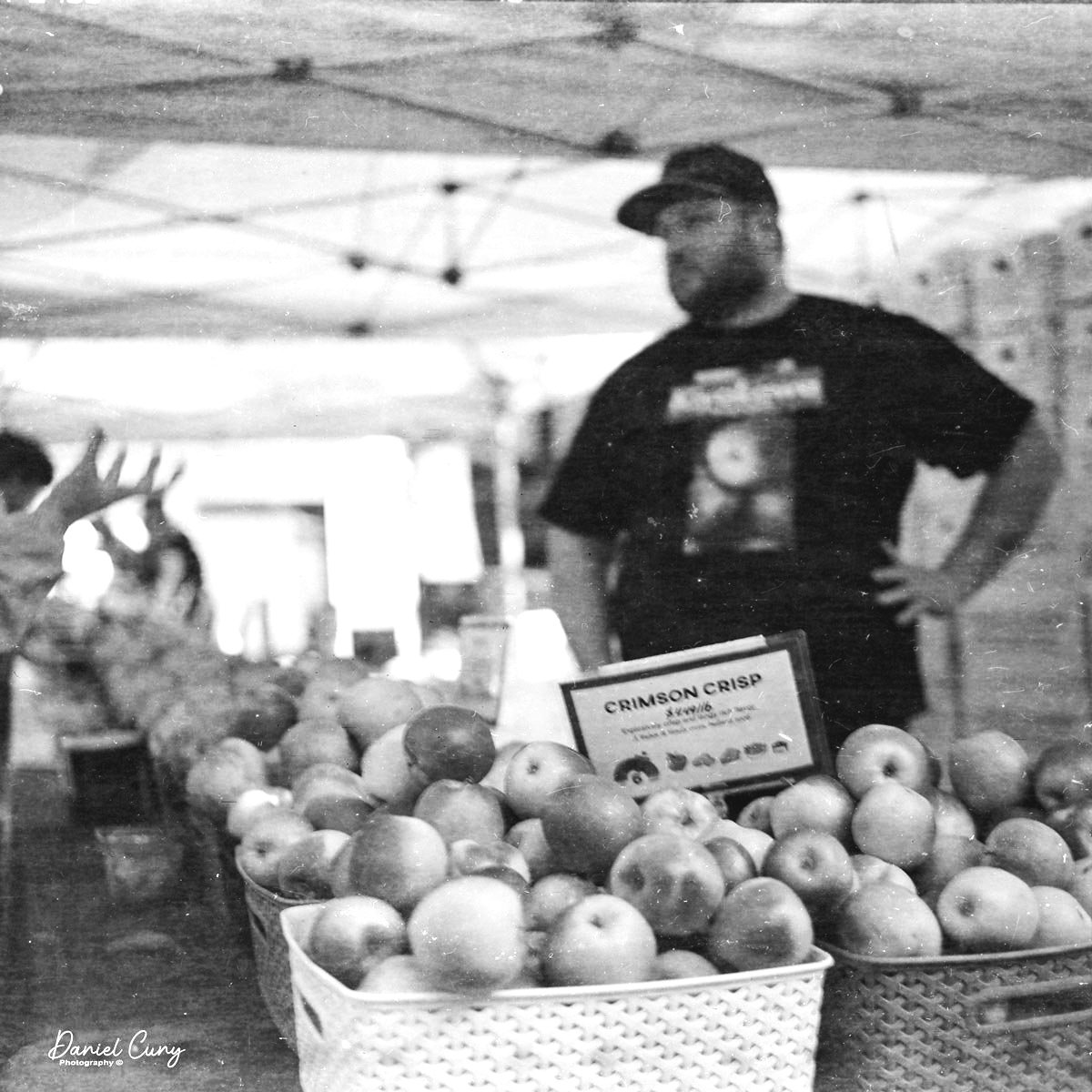
I loaded my Minolta-35 camera with a roll of Ilford Pan F Plus 50 ISO black-and-white film. I wanted to use a slow speed to see how the camera would perform in lower-light situations. I also had my trusty Sekonic L-308 meter with me to achieve accurate exposures. I knew I could always count on Sekonic to give precise light readings.
Now that I had film loaded into the newly serviced camera, I walked through my yard and neighborhood to take photos with the Minolta-35 camera. Here are a few of the images I took on my walk.
My Conclusion:
The camera was enjoyable to photograph with. The rangefinder was bright and accurate. I tried many slow shutter speeds to see how the camera performed under these low-light circumstances. I had a great time using this camera and want to continue using it. The overhaul made a tremendous difference; without the black paint on the camera, it also looks terrific.
Thank you for taking a few minutes from your busy schedule to read about this excellent rangefinder camera from Minolta
Until next week, please be safe.